 |
 |
- Search
| Healthc Inform Res > Volume 27(4); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objectives
Despite the growing use of mobile health (mHealth), certain barriers seem to be hindering the use of mHealth applications in healthcare. This article presents a systematic review of the literature on barriers associated with mHealth reported by healthcare professionals.
Methods
This systematic review was carried out to identify studies published from January 2015 to December 2019 by searching four electronic databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar). Studies were included if they reported perceived barriers to the adoption of mHealth from healthcare providersŌĆÖ perspectives. Content analysis and categorization of barriers were performed based on a focus group discussion that explored researchersŌĆÖ knowledge and experiences.
Results
Among the 273 papers retrieved through the search strategy, 18 works were selected and 18 barriers were identified. The relevant barriers were categorized into three main groups: technical, individual, and healthcare system. Security and privacy concerns from the category of technical barriers, knowledge and limited literacy from the category of individual barriers, and economic and financial factors from the category of healthcare system barriers were chosen as three of the most important challenges related to the adoption of mHealth described in the included publications.
Conclusions
mHealth adoption is a complex and multi-dimensional process that is widely implemented to increase access to healthcare services. However, it is influenced by various factors and barriers. Understanding the barriers to adoption of mHealth applications among providers, and engaging them in the adoption process will be important for the successful deployment of these applications.
In recent years, cellphones have become an integral part of modern life, and mobile health (mHealth) apps have found their place in the healthcare system [1]. Nonetheless, the success of mHealth technology as a tool to improve healthcare service delivery processes depends on its adoption by healthcare providers [2,3].
Increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and providing healthcare in the least time with the minimum risk are the most important benefits of mHealth [4]. Furthermore, mHealth platforms include multiple functionalities such as education for patients and healthcare providers, diagnostic support, operative planning, postoperative care, and follow-up management [5ŌĆō7].
With the increasing use of smartphones and the growing number of healthcare applications in multiple domains, mHealth is expected to encompass tools that will play an important role in healthcare professionalsŌĆÖ decision-making [8,9]. Nevertheless, it appears that some mHealth applications remain underused by healthcare professionals [10].
Most healthcare providers, particularly physicians, resist using electronic health technologies such as Electronic Health Records, patient portals, online health information, telemedicine, and mHealth [2]. Implementation of these technologies, especially mHealth, implies changes in organizational structures and processes, which often encounter various forms of resistance [11]. Resistance to change is an important barrier hindering the use of new technologies by healthcare providers [12]. Some common barriers include technical, individual, and organizational factors.
Although barriers associated with mHealth adoption in healthcare settings have been addressed in the literature, few studies have systematically reviewed factors influencing the adoption of mHealth. Therefore, there is no consensus on the categorization of barriers to mHealth adoption. Two studies have highlighted barriers and facilitators regarding patientsŌĆÖ and the publicŌĆÖs ability to engage with and use digital health interventions such as telehealth systems, mHealth applications, patient portals, and personal health records [13,14]. To the authorsŌĆÖ knowledge, only one systematic review has been conducted on factors that could facilitate or limit healthcare providersŌĆÖ utilization of mHealth in their work [2]. In that review, the analyzed data were retrieved from four databases between 2000 and 2014. Our study builds upon that previous work, with the aim of conducting a systematic review of more recent literature on barriers associated with mHealth reported by healthcare professionals and identifying the most important barriers.
We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items in Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) protocol. We conducted a systematic literature search of four electronic databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar) to identify studies published between January 2015 and December 2019. We also searched the references of the included publications to identify additional relevant studies. We followed the PICO (population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes) model as a search strategy tool that improves literature searches: (1) the population consisted of healthcare providers (e.g., professionals, physicians, practitioners, providers, residents, clinicians, nurses, midwives, health workers, specialists, dentists, pharmacists, dieticians, physiotherapists, cardiologists, surgeons, gynecologists, ophthalmologists, psychiatrists, and opticians); (2) the intervention was mHealth technology; (3) the comparison was the absence of mHealth technology; and (4) the outcome was reported barriers to adoption of mHealth technology by healthcare providers.
Therefore, the search query included three categories of keywords and their synonyms: barriers, adoption, and mHealth, the definitions of which are presented below.
First, mHealth is a subset of electronic health and refers to the use of portable wireless devices capable of transmitting, storing, processing, and retrieving real-time and non-real-time data between patients and healthcare providers [6,15]. Technology adoption refers to the acceptance, integration, and use of new technology in society and focuses on how a technologyŌĆÖs attributes affect an individualŌĆÖs perception of that technology [16]. Barriers are rules, problems, and similar structures that prevent people from doing something, or limit what they can do [6]. Papers containing these keywords in the title or abstract were searched. The search terms and search strategy are described in Table 1.
First, duplicate citations across databases were identified and excluded using EndNote X7.8 (Thomson Reuters, Toronto, Canada) and a manual revision was done for verification. If a study was reported in more than one publication and presented the same data, we only included the most recent publication. In the next step, articlesŌĆÖ abstracts and titles were reviewed according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Screening of titles and abstracts was independently conducted by two medical informatics researchers, both of whom are fully versed in mHealth and healthcare systems due to their expertise. The full texts of articles identified as relevant to the objectives were reviewed by the same two researchers. Any disagreement between the researchers was resolved by discussion.
We included articles in this review if they: (1) were full-text journal articles (we excluded abstracts); (2) were published in English; (3) were published in a recent 5-year period (2015ŌĆō2019); (4) reported barriers to mHealth adoption by healthcare providers.
We excluded articles from this review if they: (1) were reviews or gray literature (e.g., conference papers); (2) did not mention the use of mHealth technology; (3) reported mHealth adoptionŌĆÖ barriers from patientsŌĆÖ perspectives; (4) did not address barriers to using mHealth technology.
To extract data and ensure the validity of gathered information, two authors (SZ and TB) extracted barriers to mHealth adoption from all included studies. The corresponding author (AY) then checked the accuracy of the extracted data. In case of any discrepancies, meetings were held to compare our findings and resolve disagreements by discussion.
A focus group discussion was then held with the participation of all authors. Based on the nature of the identified barriers and the opinions of the experts participating in the meeting, the barriers were grouped into three main categories (technical, individual, and healthcare system). Next, each of the identified barriers was assigned to one of the three major categories based on participantsŌĆÖ knowledge and experiences. In this study, due to the nature of the data extracted from the included studies, there was no need for a quality assessment.
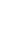
In total, 273 articles were retrieved using the search strategy. Ninety-two duplicates were excluded. After removing the duplicates, the abstracts and titles of 181 articles were studied with respect to the inclusion criteria. At this stage, 137 articles were excluded due to irrelevance of the article title or abstract. The full-texts of 44 articles, which were identified as relevant to the objectives, were investigated. Eighteen articles considered to be eligible were finally included. Three of these articles were found from Google Scholar. Finally, considering the duplication of barriers in different articles, 167 barriers were extracted from the 18 selected articles. The results of the literature search are shown in Figure 1, and the details of each article are summarized in Table 2 [1,17ŌĆō33].
The relevant barriers were categorized into three main groups: technical, individual, and healthcare system. The major categories of barriers to mHealth adoption by healthcare providers are summarized in Figure 2. Technical barriers included eight factors: the lack of existing technology, concerns about regulation and efficacy of applications, security and privacy concerns, user-friendliness, compatibility with the workflow, connectivity speed, a lack of interoperability, and integration with other systems. Individual barriers included five factors: a lack of physician support, resistance to change, difficulty understanding the technology, human appeal, and knowledge and limited literacy. Healthcare system barriers included five factors: legal barriers, reimbursement and accountable care organizations, economic and financial factors, lack of health system policies, and lack of standards.
Healthcare providers, especially physicians, have mentioned a lack of existing technology as one of the largest barriers to greater use of mHealth [17,19]. Technology refers to the collection of techniques, skills, methods, evidence, and processes put into practical use to solve problems [34]. Despite widespread technological advances, there is currently a lack of sufficient evidence-based and specific processes that support the adoption of new technologies, especially mHealth [35].
In most cases, some aspects are not taken into consideration when developing and releasing a new technology or application. One of the most important considerations is privacy and security, especially in apps that deal with patientsŌĆÖ data regarding their personal and health status, such as Electronic Health Records [25,29,36,37].
Mobile health platforms offer significant opportunities to improve physician-patient communication and patientsŌĆÖ self-care if they are sufficiently usable [4,38]. These apps have become an essential part of the healthcare field. Their user-friendliness is an essential factor for healthcare providersŌĆÖ satisfaction. The majority of reports on mHealth apps illustrate that a lack of user-friendliness can lead to failure [18,39].
Interoperability refers to the ability of information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, and integrate health data between more than one organization and/or setting of care. A lack of interoperability is often cited as a barrier by healthcare providers because of the burden of their work processes and healthcare costs [18,23,40,41].
According to the report released by the World Health Organization (WHO), the use of mHealth technology has changed the image of healthcare delivery worldwide [42]. However, the development of mHealth in the healthcare industry has received little attention from physicians, although healthcare providersŌĆÖ familiarity with and adoption of mHealth technology have a positive impact on its expansion and success [17,21,29].
Mobile technology is changing the way people interact with each other. mHealth technology is used to improve the effectiveness of communication between healthcare providers and their patients [18]. However, the lack of face-to-face human interactions in mHealth technology is a major obstacle to its adoption [17,23,39].
Legal issues are closely related to the trust issues of healthcare providers. In most countries, because of a lack of legislation, physicians do not trust mHealth applications, and therefore do not accept and work with them. Sands [43] discussed health data sharing and dissemination via mobile devices as physiciansŌĆÖ main concerns due to the lack of corresponding legislation [11,17,18,23].
Reimbursement is another concern of healthcare providers when using new technologies such as mHealth applications for care delivered through these devices. Appropriate reimbursement would require some changes to rules and workflows to overcome some of the current barriers and limitations [17,18,40,41].
These factors refer to the financial resources needed to expand mHealth in rural areas in developing countries. The provision of the tools, equipment, and technological infrastructure to prepare and use these new technologies is not possible without funding resources and economic support [17,19,20,22].
A standard is an agreed-upon way of doing something, and standards are a key factor for achieving interoperability of healthcare systems and technologies. In addition, healthcare providers believe that a lack of standards, such as identifier standards, messaging standards, structure and content standards, clinical terminology and classification standards, and security and access control standards, hinder the development of mHealth technology. Therefore, technological standards for mHealth need to be developed [4,21,24,28,29].
In this review, we identified the literature on common barriers that could limit health professionalsŌĆÖ use of mHealth in their work. Healthcare providers, like many other people, may have a mobile phone or other handheld devices, but this fact does not necessarily mean that they use mobile phones for work purposes. However, given the global focus on mHealth technology, it is important to recognize the factors that affect mHealth adoption by healthcare providers.
The main findings of this systematic review highlight that the identified barriers to mHealth adoption could be classified into three main categories or levels: technical, individual, and healthcare system. Individual-level barriers are directed towards clinicians, physicians, and healthcare providers [44]. Technical-level barriers focus more on network, hardware, and software applications related to the mobile technology devices that clinicians, physicians, and healthcare providers use in the healthcare system [17]. Healthcare system-level barriers refer to managerial attitudes in the system, as well as healthcare policy, standards, and aspects of the financial and reimbursement system [45]. Security and privacy concerns at the technical level, knowledge and limited literacy at the individual level, and economic and financial factors at the healthcare system level were chosen as three of the most important barriers related to the adoption of mHealth in the included publications.
The results of this study are in line with those of the WHO report in 2011, which revealed that security, cost, interoperability, scalability, and lack of local knowledge were the top barriers to mHealth implementation and use. The WHO emphasized that these barriers must be removed before mHealth projects are expanded beyond the pilot stages [26].
The present findings are consistent with those of the systematic review conducted by Gagnon et al. [2], who found that several factors were associated with mHealth adoption at the individual, organizational, and contextual levels. The most important factors identified were privacy and security issues, usefulness and ease of use, time, cost, knowledge of mHealth technology, interactions between healthcare providers and patients, design, and technical concerns.
Our findings also align with those of Laxman et al. [17], who demonstrated mHealth barriers and categorized them as belonging to two levels (system and individual). User-friendliness and a lack of physician support were identified as individual-level barriers, while system-level barriers included security, difficulty understanding the technology, concerns about the regulation and efficacy of applications, human appeal, lack of financial support, and connectivity.
Security and privacy concerns are a major challenge to mHealth adoption [18]. Although mobile technology has revolutionized the way we access information at any time and any place in our lives, consumers of this informationŌĆöand especially healthcare providersŌĆöare concerned about the privacy and security of health-related information. Therefore, healthcare system managers and policymakers must develop appropriate programs, approaches, and policies to ensure privacy and security [46].
The adoption of mHealth offers many benefits to healthcare providers, patients, and managers, as well as other stakeholders. From these healthcare consumersŌĆÖ perspectives, mHealth facilitates access to high-quality healthcare service, communication between patients and clinicians, and collaboration between physicians [47]. Higher-quality and more rapid care can be provided because healthcare providers can access consumersŌĆÖ health information whenever they need it. However, many perceived factors and barriers have hampered the widespread adoption and implementation of mHealth [48]. It will be a time-consuming and challenging process for healthcare providers to overcome these barriers [11].
A major strength of our study is its unique search approach. In the search strategy, we combined elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e.g., the use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, and inference techniques) to achieve the goals of breadth and depth of understanding and corroboration, and we then used the findings of the identified studies in an integrative manner in our synthesis. Finally, we presented a new classification of barriers related to mHealth adoption by healthcare providers.
Our study has two main limitations. First, we concentrated only on mHealth adoption by healthcare professionals in this review, although it is also important to consider the adoption of mHealth technology in the healthcare system from the perspective of other stakeholders, such as patients and their companions. As Menachemi has pointed out, the opposition and resistance of each of these stakeholders can slow the process adoption [49]. Another limitation of this study is that we did not propose and evaluate facilitators that would increase the adoption of mHealth technology. It is possible that identifying and using facilitators may help overcome the barriers to adopting mHealth technology. This article can be a starting point for future research aiming to identify and evaluate barriers and facilitators of mHealth from the perspective of other health stakeholders.
In conclusion, mHealth adoption is a complex and multidimensional process that is widely implemented to increase access to healthcare services. However, it is influenced by a variety of factors and barriers at the individual, technical, and healthcare system levels. Based on the barriers to adoption identified in this review, security and privacy concerns, knowledge and limited literacy, and economic and financial factors were identified as the top barriers related to the adoption of mHealth. While some authors have focused on the barriers of other information and communication technologies, this systematic review empowered us to identify factors that are specific to mHealth. Understanding barriers to adoption of mHealth applications among providers and engaging them in the adoption process will also be important for the successful implementation of these applications. Therefore, new mHealth applications should focus on these factors in order to facilitate the adoption of mHealth tools to support patient care and to improve their outcomes.
Table┬Ā1
Search terms and search strategy
Table┬Ā2
Barriers to mHealth adoption
| Study | Year | Country | Type of study | Barriers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical barriers | Individual barriers | Healthcare system barriers | ||||
| Laxman et al. [17] | 2015 | New Zealand | Qualitative |
Lack of existing technology Regulation and efficacy of application Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors |
| Gleason [18] | 2015 | USA | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration |
Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| OŌĆÖConnor & OŌĆÖDonoghue [19] | 2015 | United Kingdom | Qualitative |
Lack of existing technology User-friendliness Connectivity speed |
Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Medhanyie et al. [20] | 2015 | Ethiopia | Quantitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Problem with devices |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Lavariega et al. [21] | 2016 | Mexico | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Nebeker et al. [23] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Lack of interoperability and integration |
Lack of physician support Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers |
| Kao & Liebovitz [24] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration |
Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| Van Heerden et al. [25] | 2017 | South Africa | Quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and Integration Problems with devices |
Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Abelson et al. [26] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Problems with devices User-friendliness |
Human appeal Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Faber et al. [27] | 2017 | Netherlands | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Lack of interoperability and integration Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Knowledge and limited literacy |
Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Graves et al. [28] | 2018 | Canada | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration Problems with devices |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Lack of standards |
| Rassi et al. [29] | 2018 | United Kingdom | Qualitative or quantitative |
User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Spann & Stewart [30] | 2018 | United Kingdom | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness Connectivity speed Compatibility with the workflow Security and privacy concerns Problems with devices |
Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy Difficulty understanding the technology |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Bally & Cesuroglu [31] | 2019 | Netherlands | Qualitative or quantitative |
Lack of existing technology Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Lack of interoperability and integration |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| Zhou et al. [32] | 2019 | USA | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness |
Difficulty understanding the technology |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Byambasuren et al. [1] | 2019 | Australia | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Lack of existing technology Lack of interoperability and integration User-friendliness |
Knowledge and limited literacy Difficulty understanding the technology |
- |
| Anastasiadou et al. [33] | 2019 | Spain | Qualitative |
Compatibility with the workflow Lack of interoperability and integration Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness |
Knowledge and limited literacy Lack of physician support Difficulty understanding the technology Resistance to change Human appeal |
Lack of health systems policies Economic and financial factors Lack of standards Reimbursement care organizations |
References
1. Byambasuren O, Beller E, Glasziou P. Current knowledge and adoption of mobile health apps among Australian general practitioners: survey study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019;7(6):e13199.


2. Gagnon MP, Ngangue P, Payne-Gagnon J, Desmartis M. m-Health adoption by healthcare professionals: a systematic review. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2016;23(1):212-20.


3. Garavand A, Samadbeik M, Kafashi M, Abhari S. Acceptance of health information technologies, acceptance of mobile health: a review article. J Biomed Phys Eng 2017;7(4):403-8.



4. Ventola CL. Mobile devices and apps for health care professionals: uses and benefits. P T 2014;39(5):356-64.



5. Hamilton EC, Saiyed F, Miller CC 3rd, Eguia A, Fonseca AC, Baum GP, et al. The digital divide in adoption and use of mobile health technology among caregivers of pediatric surgery patients. J Pediatr Surg 2018;53(8):1478-93.


6. Baniasadi T, Niakan Kalhori SR, Ayyoubzadeh SM, Zakerabasali S, Pourmohamadkhan M. Study of challenges to utilise mobile-based health care monitoring systems: a descriptive literature review. J Telemed Telecare 2018;24(10):661-8.


7. Zahmatkeshan M, Zakerabasali S, Farjam M, Gholampour Y, Seraji M, Yazdani A. The use of mobile health interventions for gestational diabetes mellitus: a descriptive literature review. J Med Life 2021;14(2):131-41.



8. Winters N, Langer L, Geniets A. Scoping review assessing the evidence used to support the adoption of mobile health (mHealth) technologies for the education and training of community health workers (CHWs) in low-income and middle-income countries. BMJ Open 2018;8(7):e019827.



9. Kaphle S, Chaturvedi S, Chaudhuri I, Krishnan R, Lesh N. Adoption and usage of mHealth technology on quality and experience of care provided by frontline workers: observations from rural India. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2015;3(2):e61.



10. Gagnon MP, Desmartis M, Labrecque M, Car J, Pagliari C, Pluye P, et al. Systematic review of factors influencing the adoption of information and communication technologies by healthcare professionals. J Med Syst 2012;36(1):241-77.


11. Lluch M. Healthcare professionalsŌĆÖ organisational barriers to health information technologies: a literature review. Int J Med Inform 2011;80(12):849-62.


12. Nilsen ER, Dugstad J, Eide H, Gullslett MK, Eide T. Exploring resistance to implementation of welfare technology in municipal healthcare services: a longitudinal case study. BMC Health Serv Res 2016;16(1):657.




13. OŌĆÖConnor S, Hanlon P, OŌĆÖDonnell CA, Garcia S, Glanville J, Mair FS. Barriers and facilitators to patient and public engagement and recruitment to digital health interventions: protocol of a systematic review of qualitative studies. BMJ Open 2016;6(9):e010895.



14. Scott Kruse C, Karem P, Shifflett K, Vegi L, Ravi K, Brooks M. Evaluating barriers to adopting telemedicine worldwide: a systematic review. J Telemed Telecare 2018;24(1):4-12.


15. Adibi S. Link technologies and BlackBerry mobile health (mHealth) solutions: a review. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 2012;16(4):586-97.


16. Godoe P, Johansen T. Understanding adoption of new technologies: technology readiness and technology acceptance as an integrated concept. J Eur Psychol Stud 2012;3(1):38-52.

17. Laxman K, Krishnan SB, Dhillon JS. Barriers to adoption of consumer health informatics applications for health self management. Health Sci J 2015;9(5):7.

18. Gleason AW. mHealth: opportunities for transforming global health care and barriers to adoption. J Electron Resour Med Libr 2015;12(2):114-25.

19. OŌĆÖConnor Y, OŌĆÖDonoghue J. Contextual barriers to mobile health technology in African Countries: a perspective piece. J Mob Technol Med 2015;4(1):31-4.

20. Medhanyie AA, Little A, Yebyo H, Spigt M, Tadesse K, Blanco R, et al. Health workersŌĆÖ experiences, barriers, preferences and motivating factors in using mHealth forms in Ethiopia. Hum Resour Health 2015;13(1):2.



21. Lavariega JC, Garza R, Gomez LG, Lara-Diaz VJ, Silva-Cavazos MJ. EEMI: an electronic health record for Pediatricians: Adoption barriers, services and use in Mexico. Int J Healthc Inf Syst Inform 2016;11(3):57-69.

22. Rajan JV, Moura J, Gourley G, Kiso K, Sizilio A, Cortez AM, et al. Understanding the barriers to successful adoption and use of a mobile health information system in a community health center in S├Żo Paulo, Brazil: a cohort study. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2016;16(1):146.



23. Nebeker C, Murray K, Holub C, Haughton J, Arredondo EM. Acceptance of mobile health in communities underrepresented in biomedical research: barriers and ethical considerations for scientists. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2017;5(6):e87.



24. Kao CK, Liebovitz DM. Consumer mobile health apps: current state, barriers, and future directions. PM R 2017;9(5S):S106-S115.


25. van Heerden A, Harris DM, van Rooyen H, Barnabas RV, Ramanathan N, Ngcobo N, et al. Perceived mHealth barriers and benefits for home-based HIV testing and counseling and other care: qualitative findings from health officials, community health workers, and persons living with HIV in South Africa. Soc Sci Med 2017;183:97-105.



26. Abelson JS, Kaufman E, Symer M, Peters A, Charlson M, Yeo H. Barriers and benefits to using mobile health technology after operation: a qualitative study. Surgery 2017;162(3):605-11.


27. Faber S, van Geenhuizen M, de Reuver M. eHealth adoption factors in medical hospitals: a focus on the Netherlands. Int J Med Inform 2017;100:77-89.


28. Graves M, Doucet S, Dube A, Johnson M. Health professionalsŌĆÖ and patientsŌĆÖ perceived barriers and facilitators to collaborating when communicating through the use of information and communication technologies. J Interprof Educ Pract 2018;10:85-91.

29. Rassi C, Gore-Langton GR, Gidudu Walimbwa B, Strachan CE, King R, Basharat S, et al. Improving health worker performance through text messaging: a mixed-methods evaluation of a pilot intervention designed to increase coverage of intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy in West Nile, Uganda. PLoS One 2018;13(9):e0203554.



30. Spann A, Stewart E. Barriers and facilitators of older peopleŌĆÖs mHealth usage: a qualitative review of older peopleŌĆÖs views. Hum Technol 2018;14(3):264-96.

31. Bally EL, Cesuroglu T. Toward integration of mHealth in primary care in the Netherlands: a qualitative analysis of stakeholder perspectives. Front Public Health 2020;7:407.



32. Zhou L, Bao J, Watzlaf V, Parmanto B. Barriers to and facilitators of the use of mobile health apps from a security perspective: mixed-methods study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019;7(4):e11223.



33. Anastasiadou D, Folkvord F, Serrano-Troncoso E, Lupianez-Villanueva F. Mobile health adoption in mental health: user experience of a mobile health app for patients with an eating disorder. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019;7(6):e12920.



34. Wahab SA, Rose RC, Osman SI. Defining the concepts of technology and technology transfer: a literature analysis. Int Bus Res 2012;5(1):61-71.

35. Steinhubl SR, Muse ED, Topol EJ. The emerging field of mobile health. Sci Transl Med 2015;7(283):283rv3.



36. Martinez-Perez B, de la Torre-Diez I, Lopez-Coronado M. Privacy and security in mobile health apps: a review and recommendations. J Med Syst 2015;39(1):181.


38. Zahra F, Hussain A, Mohd H. Usability factors of mobile health application for chronic diseases. AIP Conf Proc 2016;1761(1):020108.

39. Dunlop M, Brewster S. The challenge of mobile devices for human computer interaction. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 2002;6:235-6.

40. LeRouge C, Garfield MJ. Crossing the telemedicine chasm: have the U.S. barriers to widespread adoption of telemedicine been significantly reduced? Int J Environ Res Public Health 2013;10(12):6472-84.



41. Weinstein RS, Lopez AM, Joseph BA, Erps KA, Holcomb M, Barker GP, et al. Telemedicine, telehealth, and mobile health applications that work: opportunities and barriers. Am J Med 2014;127(3):183-7.


42. Mehdipour Y, Ebrahimi S, Khammarnia M, Alipour J, Karimi A. The acceptance of mobile health services by physicians: the case of Iran. Shiraz E-Med J 2018;19(Suppl):e66316.

43. Sands DZ. Help for physicians contemplating use of e-mail with patients. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2004;11(4):268-9.



44. McDaniel AM, Schutte DL, Keller LO. Consumer health informatics: from genomics to population health. Nurs Outlook 2008;56(5):216-223e3.


45. Linsky A, Zimmerman KM. Provider and system-level barriers to deprescribing: interconnected problems and solutions. Public Policy Aging Rep 2018;28(4):129-33.

46. Zakerabasali S, Safdari R, Kadivar M, Rostam Niakan Kalhori S, Mokhtaran M, Karbasi Z, et al. Neonatal abstinence syndrome: a systematic review of current databases and registries. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2021;34(6):979-92.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in Healthc Inform Res
-
Value-Based Health Technology Assessment and Health Informatics2017 July;23(3)