 |
 |
- Search
| Healthc Inform Res > Volume 21(2); 2015 > Article |
Abstract
Objectives
New methods for obtaining appropriate information for users have been attempted with the development of information technology and the Internet. Among such methods, the demand for systems and services that can improve patient satisfaction has increased in hospital care environments.
Methods
In this paper, we proposed the Hospital Exam Reservation System (HERS), which uses the data mining method. First, we focused on carrying clinical exam data and finding the optimal schedule for generating rules using the multi-examination pattern-mining algorithm. Then, HERS was applied by a rule master and recommending system with an exam log. Finally, HERS was designed as a user-friendly interface.
Results
HERS has been applied at the National Cancer Center in Korea since June 2014. As the number of scheduled exams increased, the time required to schedule more than a single condition decreased (from 398.67% to 168.67% and from 448.49% to 188.49%; p < 0.0001). As the number of tests increased, the difference between HERS and non-HERS increased (from 0.18 days to 0.81 days).
Conclusions
It was possible to expand the efficiency of HERS studies using mining technology in not only exam reservations, but also the medical environment. The proposed system based on doctor prescription removes exams that were not executed in order to improve recommendation accuracy. In addition, we expect HERS to become an effective system in various medical environments.
The Hospital Information System (HIS) has been developed based on the action and receipt of patient orders. Recently, various studies and developments have emerged for the education, management, and treatment of patients. Such information systems offer essential information to medical service providers to improve decision-making, and communication between medical service providers and consumers. The direction of medical information has grown toward the improvement of patient satisfaction and high-quality services. Furthermore, the need to provide effective medical information services has increased, which corresponds to the latest information and communications technology, such as mobile and individually customized services [1]. Above all, long waiting times (20.2%) is the main cause of patient dissatisfaction, along with expensive medical bills (24.7%) and unsatisfactory treatments (20.7%) [2,3,4]. From the perspective of patients, waiting time is important when evaluating the quality of medical services [5,6,7,8]. Therefore, almost all medical institutions attempt to find solutions to control the patient service process. This corresponds to the utilization of an appointment policy to control visiting times and scheduling rules for an efficient patient service sequence [9]. Most large hospitals have scheduling rules based on reservation policy and client relationship management (CRM). In addition, hospital staff can effectively manage integrated reservations through scheduling rules [10,11]. Thorough education in medical environments and examination orders are required for reservation counselors. Such education can help to decrease the ratio of patient complaints because patient-centered schedule management depends on the reservationist's skill. The administration of contrast media into the blood vessels should be scheduled when blood tests are taken [12,13]. Therefore, reservation management systems were designed to offer a user-centric user interface (UI) to prevent human error and improve customer satisfaction [14]. First, rules were defined using the sequential pattern of mining techniques through the pattern analysis of exams conducted on each outpatient [15]. Second, a one & nonstop environment through master management of exams and a multi-reservation viewer were designed to manage difficulties and exam constraints [16]. Recommendation algorithms consist of content-based algorithms and rule based algorithms. Content-based algorithms can easily reflect the properties and usages of the recommended subjects. In this study, we used a rule-based algorithm because it could cause problems, such as the complexity of the calculation and inaccuracy of new user and definitions of the terms. There are several types of the rule-based algorithms, such as online convergence detection (OCD), set oriented mining (SETM), direct hashing and pruning (DHP). However, we used an apriori algorithm because it is easy for an apriori algorithm to understand, implement, and generate a proper result to find a set of frequent items in the binary association rules. Because of the small amount of contents and the lack of a need for complicated calculation, reservation and examination in the hospital environment did not require a systemic response in accordance with the pattern. The apriori algorithm was able to make a recommendation in a short time, and this advantage could overcome the limitations of scalability and sparsity. The set of items called market basket analysis could be classified as exams, so it is proper for them to be applied in the examination reservation part of the general hospital environment. However, this study did not focus on the performance of a rule-based algorithm [15,17,18,19,20].
If there are multiple exams to be performed, the order is important. For example, when a given patient has fasted, all exams that require fasting should be performed simultaneously. Furthermore, as previously mentioned, the administration of contrast media into the blood vessels should be scheduled when blood tests are taken. Moreover, for examinations that require radioactive isotopes, the examination sequence can affect the image quality. For this reason, sequence adjustment is an important factor not only for patients, but also to improve the quality of medical services. Thus, for most of the examination processes, medical services and patient convenience are closely related. As indicated in Table 1, the rules were compared with the constraints associated with patient examination before appointments are made. To create an appropriate schedule, examination rules had to follow the rule masters. These rules based on the exam and treatment process provided optimized services to patients in a hospital.
The existing examination reservation system, including rule management based on constraints, was extremely limited in terms of providing patient-centered convenience, such as managing examination history. Because of these problems, depending on employee skills, different results could be obtained. Therefore, as shown in Figure 1, we designed an improved HERS, which is composed of a module that uses an appointment policy for patients and a scheduling rule module that determines the sequence of medical services provided. The scheduling rule module is divided into functions for single-examination reservations and multi-examination reservations. This module can perform efficient reservations with the recommended rules using rule-mining techniques. HERS can recommend the rule master to center clinical orders, and implement the result log files from the order communication system (OCS) and electronic medical record (EMR). These processes can help HERS rule masters to be more efficient. Furthermore, the history module and CRM provides basic information for efficient patient reservation. Thus, each HERS module is designed to be able to make effective examination reservations for users and patients.
A rule is generated through a single exam, or a combination of multiple exams. To generate a combination of multiple exams, exam data is collected mainly from an actual order and its enforced time. Then, other exam data, such as drug action filtering, and the respective tests, is defined as one item. The detailed procedure can be determined through the data flow shown in Figure 2A. The apriori algorithm is applied to the database under analysis. The two phases of the apriori algorithm are highlighted. The first, referred to as the 'Itemsets' phase, is aimed at the generation of candidate itemsets built at the start from the frequent itemsets of the previous phase. In the second phase, the itemsets are used in a 'Check Support (pruning)' procedure that selects the frequent itemsets based on the support verification (check). Therefore, if the set of frequent itemsets is 'Null' the algorithm stops. As shown in Figure 2B, the gathered itemsets are added to the recommendation planning only if it is multi-exam.
HERS has been applied to the integrated medical information system at National Cancer Center (NCC) in Korea since June 2014. Every hospital environment is different. However, the implementation and experiment were designed to be representative of all hospitals. HERS implementation was focused on UI improvement and job processes in which human error could be reduced. Figure 3 shows the HERS main screen. Users (e.g., call and integrated reservation counselors, inpatient and outpatient counter members) could share jobs using one screen in the hospital. HERS was designed with an intuitive interface that focuses on job processes. In addition, the main functions are examination reservations, guidelines for examination reservations, patient information, etc. Figure 3B shows the screen for scheduling more than one examination. Users can rapidly find the desired date via the screen shown.
We selected four clinical centers out of a total of fifteen clinical centers of the NCC to search patterns of recommended information based on association rules. The extracted data was processed for outpatients using examination dates within the previous six months. The mining steps were the following:
1) The extracted data is used to create a related rule using the apriori functions of the ARULES package (R statistical program).
2) After the extraction of all association rules, the algorithm searches for the satisfied reliability setting value from the found sets.
3) The results of frequent itemsets are compared with orders from the patients' clinical practices.
4) If the extracted frequent itemsets were valid at the start of the examination reservation, HERS recommends the items.
There could be more than one recommended sequence. Furthermore, HERS recommends the closest time to the current time, and the shortest total sum of items. Consequently, we could complete an effective recommendation system. In addition, HERS could be reflected in the clinical pathway (CP) of each department.
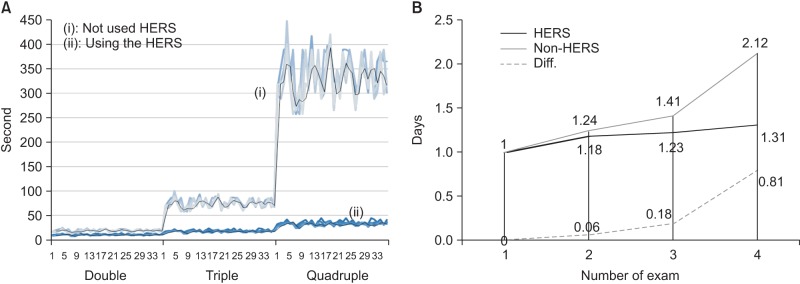
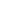
In this paper, we focused on the efficiency of patient and staff reservations in hospitals. Therefore, our analysis was performed using five weeks of log data obtained before and after the implementation of HERS for a total of ten weeks, In those ten weeks, the total number of outpatients was 38,993 for the centers for stomach, liver, lung, and large intestine (National Cancer Center, Korea). Furthermore, the number of scheduled examinations was 131,344. The average number of reserved exams was 3.07 (per a patient). If the number of scheduled exams was five or the reserved exams were not executed, these cases were excluded from the experiment (124 cases). As shown in Figure 4A, the process was continued if the number of exams for a patient was three or four. When HERS was not used increasingly, at 168.67% reservation speed, the single test ratio was 398.67%, which was a reduction of 188.49% at 448.49%. The results were analyzed through a paired t-test analysis of the same user-based results (double: mean (-8.36), Pr > | t | < 0.0001; triple: mean (-57.45), Pr > | t | < 0.0001; quadruple: mean (-303.6), Pr > | t | < because it showed 0.0001); HERS efficiency could be noted. Figure 4B, after ambulatory care, shows how strongly inspection intervals were aligned until the next patient's visit. From the extent of the reduction of the inspection schedule interval between tests, it is possible to shorten the date of the subsequent clinic visit and the total time spent at the clinic. Furthermore, it was possible to confirm that reduced spacing between examination dates is associated with an increase in the number of scheduled scans through the use of HERS, as shown in Figure 4B.
Reservation counselors could easily and rapidly manage their job through HERS. In addition, reservations for patients could be made with reduced waiting times, which had a positive effect on optimized medical services. Most mining technology-based recommendation systems have negative effects when the input values are incorrect. Therefore, their degree of recommendation was not high. Furthermore, methods based on keyword entry require numerous operations that use the weight of relationships between user and content. As a result, their recommendation performance is lower. In this paper, we proposed a recommendation system based on doctor prescriptions to overcome the aforementioned problems. The proposed system removes those exams that were not executed to improve recommendation accuracy. Moreover, we analyzed the patterns of executed exams based on the data of each department in this study. This system supported the ability to extract more accurate patterns by limiting the appropriate range and threshold. In the implementation test, many frequent items that could be used were created because the connections between exams are strengthened. The results section in HERS was limited by the number of items that could be displayed on the (association rules) orders of examination reservations to reference four items. The reason for this limitation was to prevent the concentration phenomenon of particular content with high support value. In this paper, we used an apriori algorithm. By recommending closer dates and faster times, the proposed system could provide effective service to hospital staff and patients. In addition, we proved the accuracy and efficiency of HERS through real operation in a hospital. In the future, we will research medical data mining to further improve the efficiency and accuracy of our service. HERS will be an advanced extension of various applications and services. In addition, the service will be improved to meet users' needs through continuing research.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Industrial Strategic technology development program (13313502) funded By the Ministry of Trade, industry & Energy (MI, Korea).
References
1. Felfernig A, Mandl M, Tiihonen J, Schubert M, Leitner G. Personalized user interfaces for product configuration Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces; 2010 Feb 7-10. Hong Kong, China; p. 317-320.

2. Korean Statistical Information Service. Social survey medical services dissatisfied reasons (primary response, and 13 years of age or older) [Internet]. Daejeon: Korean Statistical Information Service; c2014. cited at 2014 Dec 4. Available from: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1SS14HE111R&vw_cd=MT_OTITLE&list_id=MT_CTITLE_gE_2014&scrId=&seqNo=&lang_mode=ko&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=E1.

3. Jeong BH, Choi JT, Park SS. An implementation of medical treatment schedule guidance system for inpatients satisfaction improvement. J Korean Inst Inf Technol 2012;10(2):88-93.

4. Hwang EJ. Effects of job satisfaction and patients satisfaction on medical profit at public hospitals. Korean J Hosp Manag 2014;19(2):11-20.

5. Park SH. Analysis of factors delaying on waiting time for medical examination of outpatient on a hospital. J Korean Soc Qual Improv Health Care 2001;8(1):56-72.

6. Hwang JI. Factors influencing consultation time and waiting time of ambulatory patients in a tertiary teaching hospital. J Korean Soc Qual Assur Health Care 2006;12(1):6-16.

7. Ko YK. The Relationships among Waiting Time, Patient's Satisfaction, and Revisiting Intention of Outpatients in General Hospital. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm 2010;16(3):219-228.

8. Park IS, Kim JS, Kim SS, Kim EJ, Choi HS, Kang SH. A study on the efficient flow of health examinees. J Digit Converg 2014;12(2):379-389.

9. Lee JK, Kim MK, Ha BH. Evaluation of appointment policy and scheduling rule for a dental clinic based on computer simulation. Korean J Hosp Manag 2011;16(4):161-182.

10. Hung SY, Hung WH, Tsai CA, Jiang SC. Critical factors of hospital adoption on CRM system: organizational and information system perspectives. Decis Support Syst 2010;48(4):592-603.

11. Goldberg D, Nichols D, Oki BM, Terry D. Using collaborative filtering to weave an information tapestry. Communications of the ACM 1992;35(12):61-70.

12. Yeom JK. Kang CY. The critical factors on improvement of medical institution competitiveness. Korean J Hosp Manag 2007;12(1):1-30.

13. Anneke Fitzgerald J, Dadich A. Using visual analytics to improve hospital scheduling and patient flow. J Theor Appl Electron Commer Res 2009;4(2):20-30.

14. Cao XJ. Medical Equipment reservation system based on hospital data integration platform. Adv Mater Res 2014;912:1291-1293.

15. Wang DX, Hu XG, Liu XP, Wang H. association rules mining on concept lattice using domain knowledge Proceedings of 2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics; 2005 Aug 18-21. Guangzhou, China; p. 2151-2154.

16. Lee SY, Lee KJ. Pattern classification model design and performance comparison for data mining of time series data. J Korean Inst Intell Syst 2011;21(6):730-736.

17. Hill W, Stead L, Rosenstein M, Furnas G. Recommending and evaluating choices in a virtual community of use Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems; 1995 May 7-11. Denver, CO; p. 194-201.

18. Sarwar B, Karypis G, Konstan J, Riedl J. Item-based collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on World Wide Web; 2001 May 1-5. Hong Kong, China; p. 285-295.

Figure 1
Diagram for the National Cancer Center Hospital Exam Reservation System. OCS: order communication system, EMR: electronic medical record, CRM: client relationship management.

Figure 2
Flowchart for Hospital Exam Reservation System (HERS) data mining and flow reserve exam. EMR: electronic medical record, OCS: order communication system.

-
METRICS

- Related articles in Healthc Inform Res
-
Impacts of Hospitals' Innovativeness on Information System Outsourcing Decisions2014 April;20(2)