 |
 |
- Search
| Healthc Inform Res > Volume 23(4); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Objectives
Stress management is related to public healthcare and quality of life; an accurate stress classification method is necessary for the design of stress monitoring systems. Therefore, the goal of this study was to design a novel stress classification model using a deep learning method.
Methods
In this paper, we present a stress classification model using the dataset from the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2013 to 2015 (KNHANES VI) to analyze stress-related health data. Statistical analysis was performed to identify the nine features of stress detection, and we evaluated the performance of the proposed stress classification by comparison with several stress detection models. The proposed model was also evaluated using Deep Belief Networks (DBN).
Results
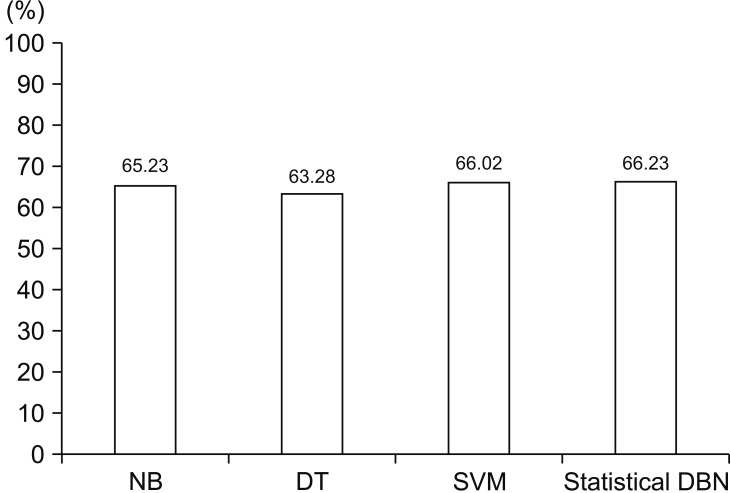
We designed profiles depending on the number of hidden layers, nodes, and hyper-parameters according to the loss function results. The experimental results showed that the proposed model achieved an accuracy and a specificity of 66.23% and 75.32%, respectively. The proposed DBN model performed better than other classification models, such as support vector machine, naive Bayesian classifier, and random forest.
Stress is a prevalent risk factor for multiple diseases; therefore, an accurate and efficient prediction of stress levels could provide a means for targeted prevention and intervention in the personal healthcare domain [12]. Therefore, to prevent the occurrence of stress related diseases, stress should be detected and managed early. In general, stress detection is assessed subjectively through surveys, and subjective health conditions tend to be evaluated higher than the actual personal health status of individuals [2]. Nonetheless, surveys are used to evaluate an individual's stress condition with ease of measurement and requiring little time. So far, there have been several domestic studies on the relationship between stress, physical activity, and lifestyle; however, most studies have been limited to specific groups and variables [234]. This is also true for previous studies on stress assessment [56]. Therefore, there is a need to develop a method for evaluating stress of an unspecified majority of people using various variables.
Stress classification and prediction techniques using machine learning methods, such as support vector machine (SVM) and k-means clustering, have been researched to improve their classification or prediction results [78]. Xu et al. [7] suggested a novel cluster-based analysis method to measure perceived stress using physiological signals, which accounts for the inter subject differences with a k-means clustering process. This method shows better evaluation accuracy than traditional methods without clustering. Sani et al. [8] introduced a method to classify stress subjects based on electroencephalography signal using SVM with a classification rate of 83.33% using radial basis function kernel function. However, these techniques require complex and stochastic signal-processing of physiological signals, which are not appropriate for the construction of prediction models based on big data and the development of deep learning technology.
Recently, prediction models have been based on artificial intelligence, and many methods using machine learning and statistics have been proposed for data mining in the healthcare sector [9]. Prediction models using these cutting-edge techniques have been used in many fields, and their value in the healthcare industry is gradually increasing. Among machine learning methods, the Deep Belief Network (DBN) is an advanced learning method using artificial neural networks that involves a high level of technology and performs well [10]. The DBN was used for handwriting recognition [1112], and image recognition [1314]. It consists of several layers of controlling restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) and uses supervised learning through back propagation after pre-training with uncoordinated learning techniques [15]. Specifically, it lies at the boundary between supervised learning (where both input and label (output) data are provided) and unsupervised learning (which learns only by input data). The technique available for both labeled and unlabeled training samples is called semi-supervised learning [16]. The DBN is used in various medical fields and is widely used in medical research because of its excellent performance [171819].
In this paper, we propose a DBN-based stress classification model that uses stress-related physical activity and lifestyle data obtained from the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI) database [20] and existing literature. First, we examined whether stress evaluation was possible by comparing the stressrelated physical activity and lifestyle data of people under 19 years and 80 years of age according to those who usually felt stressed and those who did not. Second, the DBN-based stress classification model was implemented as a feature of the physical activity and lifestyle data that were judged to be meaningful in assessing stress.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section II presents the proposed system and data processing method. Section III describes the design and implementation of the proposed stress classification by a deep learning model using the KNHANES VI dataset. Section IV discusses the experimental results and provides conclusions.
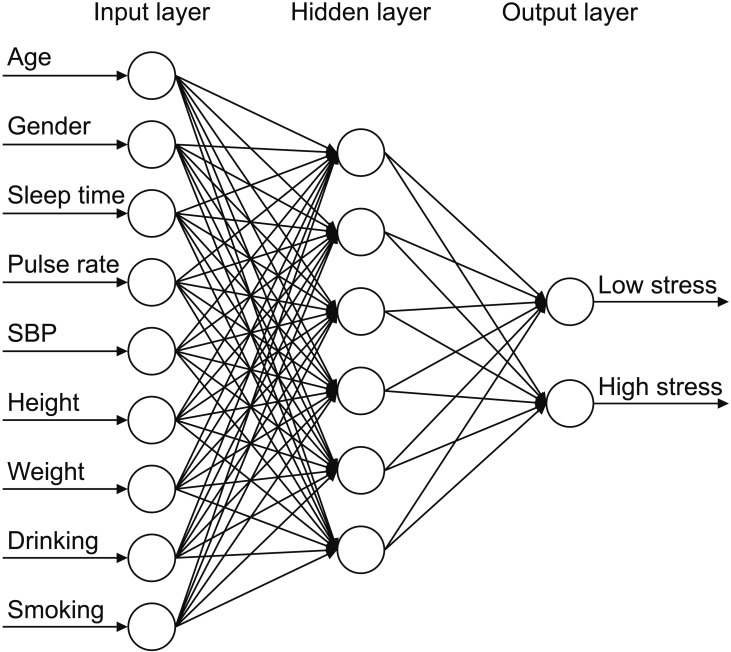
The research structure of this work is presented in Figure 1. From the KNHANES VI dataset, we selected stress-related physical activity and lifestyle data, such as sleep time, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, drinking, and smoking. The selected data were statistically analyzed to extract the variables that were considered significant for stress assessment. Clustering, DBN modeling, and model performance evaluation were performed on the extracted variables.
Clustering was conducted to investigate the possibility of stress classification through unsupervised learning with the statistical analysis data. In the DBN modeling, the statistical analysis data was used as a feature, and it was observed that stress classification was possible based on DBN. Finally, to evaluate the performance of the DBN model, we compared the stress classification results obtained using the statistical analysis data by existing models and the DBN model.
This study analyzed the records of adults aged from 19 to 80 years of age from the dataset obtained by the Health Questionnaire and Nutrition Survey conducted during the 2013–2015 KNHANES VI. In KNHANES VI (2013–2015), the questionnaire responses were classified into four categories of stress cognition. Of these, only the stress cognitive group (feeling a lot of stress and hardly feeling) was selected. The variables for classifying stress were extracted based on domestic studies on the relationship between stress, physical activity, and lifestyle. Input variables for learning included age, gender, sleeping time, pulse rate, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) as well as smoking and drinking behavior. Output variables included whether the subjects were stressed or not.
There was a total of 22,948 experimental records from KNHANES VI (2013–2015). Except for the uncertain (nonrespondent, null value) respondents, there were 14,622 records. Of the 14,622 records, the number of people who felt strongly stressed was 647, and the number of people who did not feel stressed was 2,533. Therefore, the number of stressed people was absolutely insufficient. Thus, the group that did not feel stressed was referred to as low-stress; and the group that felt very stressed was referred to as high-stress. A sample of 7 out of the 647 people who were severely stressed was excluded. The reason for this is that only 80% of the final dataset is learned with data, and we anticipated that the factor of the final dataset should be a whole number. Therefore, a total of 640 samples were extracted from the 2013–2015 data for each group, and the final dataset comprised 1,280 records.
A t-test was conducted between the low-stress and high-stress groups to compare the respective averages of age, sleep time, pulse rate, SBP, DBP, height, weight, and BMI. A chi-square test was conducted to analyze the relationship between gender, drinking and smoking variables, and stress.
IBM SPSS Statistics 24.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for the statistical analysis. A significance level of p < 0.05 for both the t-test and chi-square test was used to determine the appropriate variables to classify stress.
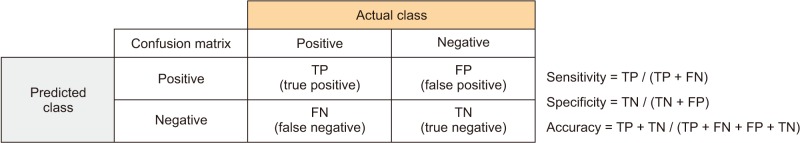
A confusion matrix was used to compare classification ability. The confusion matrix was mainly used as a performance evaluation indicator of the model. Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were measured as shown in Figure 2. The matrix was composed of the stress (low stress, high stress) classification results of the test data set.
A DBN is a deep layer neural network with multiple layers of RBM [22]. An RBM consists of one input layer into which data is input and one hidden layer where feature values are learned. All input layer and hidden layer nodes are connected to each other, but the nodes in the same layer are not connected at all. In an RBM, the nodes of the input layer learn feature values by determining how much the input data is delivered to the hidden layer according to a probability. After learning all the input values, it passes through the reconstruction process to transfer the hidden layer values to the nodes of the input layer. The result of the reconstruction process is an approximation of the input value, and learning of the RBM gradually reduces errors by repeating the above two processes. Thus, the hidden layer becomes a feature value representing the input layer [23].
A DBN is divided into two stages. The first stage is unsupervised pre-training that learns features only with input values without labels. The process is carried out as follows. The input value learns the first hidden layer x, which in turn, learns the second hidden layer. The second stage is tuning with an error back propagation algorithm using a label with supervised fine-tuning [24].
An RBM is a generative stochastic neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs. A joint configuration (v, h) of the visible nodes h and hidden nodes h can be represented by the following energy function: where vi is the binary state of visible node i, hj is the binary state of hidden node j, wij is the weight between nodes i and j, bi is the bias term of visible node i, and bj the bias term of hidden node j.
In this study, DeepLearning4J (DL4J), a Java-based toolkit for building, training, and distributing neural networks, was used in the DBN. DL4J is a domain-specific language used to configure deep neural networks, which are made of multiple layers. In the DL4J platform, hyperparameters are variables that determine how a neural network learns with Java syntax [2526]. For example, we can declare and build the configuration of visible and hidden layers through the Multilayer-Configuration object including optimal functions, such as sigmoid active function.
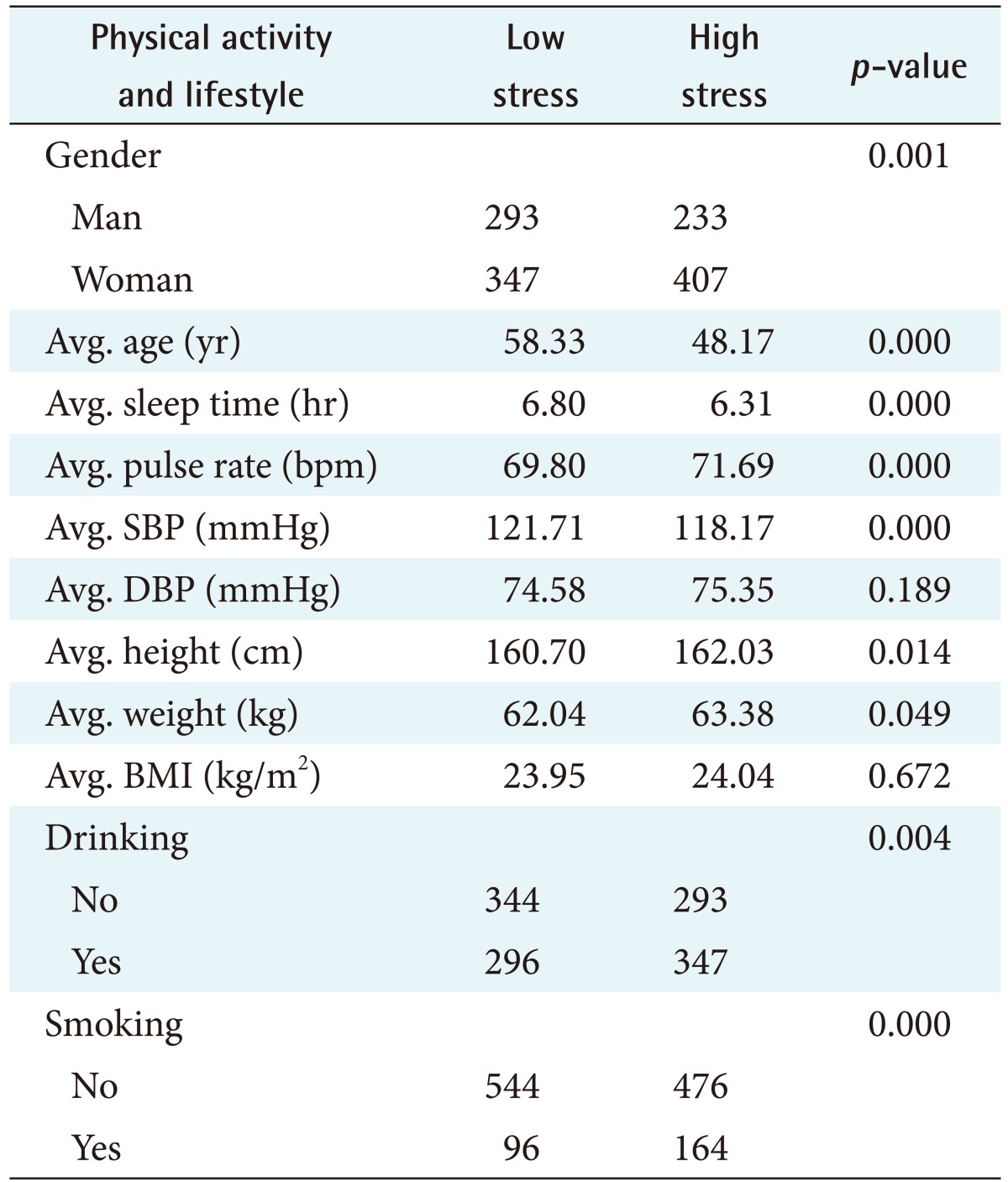
The distribution of physical activity/lifestyle records, according to the 1,280 stresses recorded in the study, is shown in Table 1. The t-test was used for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. The significance level of both tests was p < 0.05. Variables with a p-value less than 0.05 were gender, age, sleep time, pulse rate, SBP, height, weight, drinking, and smoking, making a total of nine variables related to stress.
The performance of the model depends on the number of hidden layers, nodes, and hyperparameters. To design a proper DBN-based stress classification model, we varied the number of layers, nodes and hyperparameters.
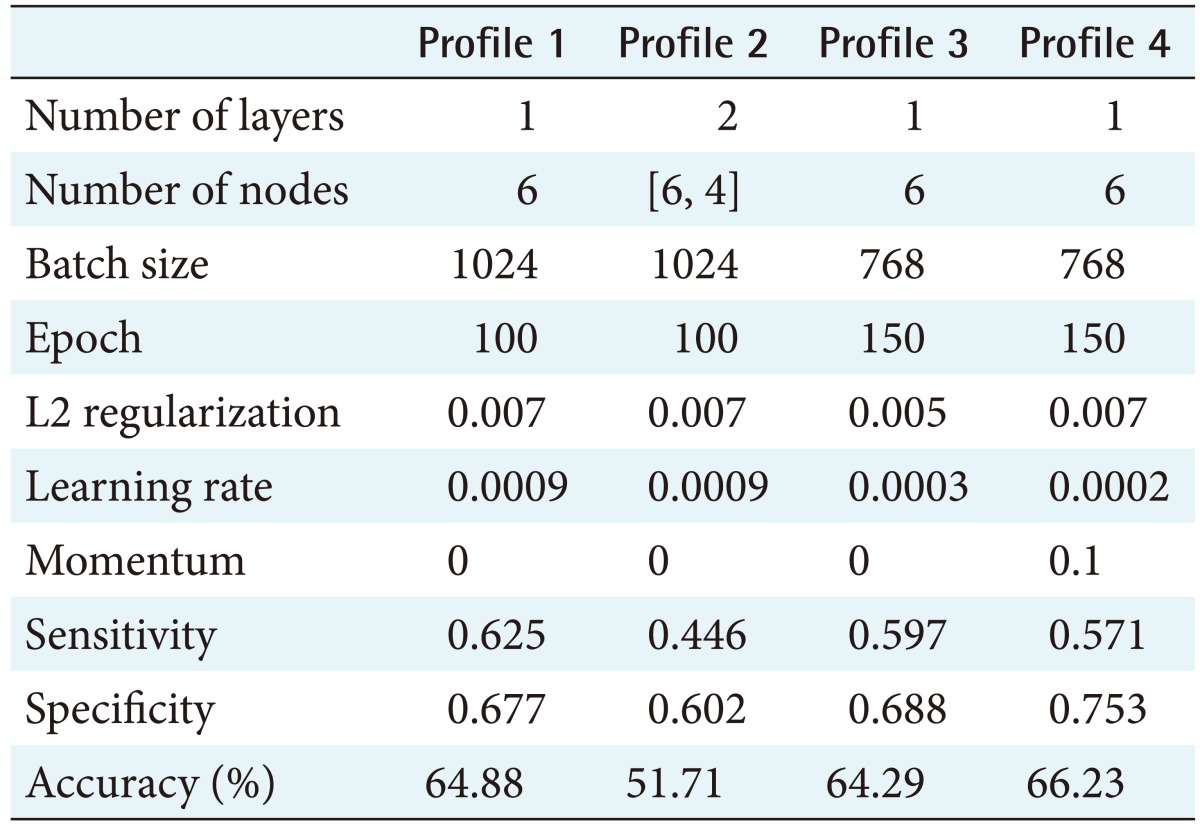
Table 2 shows the accuracy of the stress classification model according to the number of layers, nodes, and hyperparameters. Here, ‘number of layers’ is the number of layers in the DBN model, and ‘number of nodes’ is the number of nodes per layer. Additionally, ‘batch size’ refers to the grouping of multiple input data; ‘epoch’ is the number of times when training data is exhausted in one unit as 1 epoch; ‘L2 regularization’ is a commonly used normalization technique to prevent overfitting, which is overly optimized for only one dataset; ‘learning rate’ indicates the amount to update the value of the parameter; and ‘momentum’ means that parameter updates can be accelerated or decelerated [27]. Figure 3 shows the loss function graph according to the profile in Table 2. The x-axis represents the epoch, and the y-axis represents the loss. The loss function is a function that defines the error between the actual output and the expected output. Therefore, the closer the value of the loss is to zero, the more similar it is to the actual value [27]. To compare the four profiles, the graph of the loss function was equalized to the size of the epoch and the maximum and minimum losses. A comparison of the results shows that the loss value closest to 0 is that of profile 1, but considering the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, profile 4 is the optimal model.
The DBN has one hidden layer and seven input nodes (gender, age, sleep time, pulse rate, SBP, BMI, drinking, and smoking), six hidden nodes, and two output nodes (low-stress, high-stress). The hyperparameters, namely, batch size, epoch, L2 regularization, learning rate, and momentum were set to 768, 150, 0.007, 0.0002, and 0.1, respectively. The statistically analyzed dataset was divided into a training set (which comprised 80%) and a testing set (which comprised 20%). As shown in Figure 4, the measured accuracy of the stress classification model generated through learning was 66.23%.
In this study, we classified stress based on DBN using physical activity and lifestyle data. Data were obtained from the KNHNES from the 2013–2015 period. Table 1 shows that statistically significant results were obtained from the data obtained with p < 0.05 for each item (physical activity and lifestyle). The input variables of gender, age, sleep time, pulse rate, SBP, height, weight, drinking and smoking showed a statistically significant relationship with stress-related physical activity and lifestyle data. In other words, stress can be classified with a DBN model consisting of these nine input variables and two output variables (low-stress, high-stress). Setting hyperparameters in DBN research requires iterative processes and a large number of steps. In addition, the fine adjustment of the hyperparameters leads to changes in the output values, such as sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy; however, the variation is not large, and the result, which is proportional to the set value, cannot be output. Therefore, in this study, we grouped the results of the output values together as profiles during the process of observing output values with various hyperparameter values. As a result, it was confirmed that profile 4, having the best accuracy and specificity achieved excellent results. The accuracy of profile 4 was 66.23%, which is similar to that of NB (65.23%), DT (63.28), and SVM (66.02%). As the results show, SVM is time consuming because it has an accuracy similar to the DBN model, but it requires the labelling of each piece of data (correct answer) through supervised learning techniques. On the other hand, the DBN model can save time because the semi-supervised learning technology allows the use of unlabeled training samples. Therefore, although the accuracy values of the SVM and DBN model are similar, the performance of DBN model is better considering human labeling time. However, the results of this study have the following limitations. The stress classification model implemented in this work cannot be used to investigate the degree of the two subdivided cases of stress. To design a more accurate stress classification method, the degree of stress must be studied in greater detail.
In this study, the goal was to design a novel stress classification model using a deep learning method. Therefore, we presented a stress classification model, which was evaluated by using a total of 14,622 experimental records of the KNHANES VI (2013–2015) dataset to analyze stress-related health data. The statistical analysis data was used as a feature, and it was observed that stress classification was possible based on the proposed DBN model. We designed profiles based on the number of hidden layers, nodes, and hyperparameters according to the loss function results. The experimental results showed that the proposed model achieved an accuracy and a specificity of 66.23% and 75.32%, respectively. The proposed DBN model performed better than other classification models, namely, support vector machine, naive Bayesian classifier, and random forest. The model proposed in this paper was demonstrated to be effective in classifying stress detection, and it is expected to be applicable for stress prediction in stress monitoring systems.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program (No. 10073159, Developing mirroring expression based interactive robot technique by non-contact sensing and recognizing human intrinsic parameter for emotion healing through heart-body feedback) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Korea. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2017R1D-1A1B03035606).
References
1. Park JG. Articles on stress and anxiety disorder that destroy me [Internet]. Seoul: Joongdo Daily; 2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: http://www.joongdo.co.kr/jsp/article/article_view.jsp?pq=201704101817

2. Yoon JH, Lee RZ, Kim MJ. The relationship of self-rated health condition to stress recognition, health related habits, serum biochemical indices, and nutritional intakes in Korean healthy adults. Korean J Food Nutr 2017;30(1):83-95.

3. Jeon HG, Sim JM, Lee KC. An empirical analysis of effects of stress on relation between physical activity and health-related quality of life: results from KNHANES 2008 to 2013. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc 2015;16(8):5351-5363.

4. Hwang JM. Classification of health behaviors of Korean adults using physical activity, smoking, drinking and relationship with mental health. J Korea Soc Wellness 2016;11(4):369-379.

5. Lim CY, Kim KH. A Study on the assessment of stress using wireless ECG. J Korea Soc Comput Inf 2011;16(2):17-23.

6. Cho YC, Kim MS. Characteristics in HRV (heart rate variability), GSR (galvanic skin response) and skin temperature for stress estimate. J Korea Ind Inf Syst Res 2015;20(3):11-18.

7. Xu Q, Nwe TL, Guan C. Cluster-based analysis for personalized stress evaluation using physiological signals. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 2015;19(1):275-281. PMID: 25561450.


8. Sani MM, Norhazman H, Omar HA, Zaini N, Ghani SA. Support vector machine for classification of stress subjects using EEG signals Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Systems, Process and Control (ICSPC); 2014 Apr 12-14. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; p. 127-131.

9. Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 2017;42:60-88. PMID: 28778026.


10. Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 2006;18(7):1527-1554. PMID: 16764513.


11. Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006;313(5786):504-507. PMID: 16873662.


12. Lee H, Ekanadham C, Ng AY. Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2008;20:873-880.

13. Krizhevsky A, Hinton G. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images [master's thesis]. Toronto: Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto; 2009.

14. Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol PA. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning; 2008 Jul 5-9. Helsinki, Finland; p. 1096-1103.

15. Dahl GE, Yu D, Deng L, Acero A. Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 2012;20(1):30-42.

16. Mishra C, Gupta DL. Deep machine learning and neural networks: an overview. Int J Hybrid Inf Technol 2016;9(11):401-414.

17. Abdel-Zaher AM, Eldeib AM. Breast cancer classification using deep belief networks. Expert Syst Appl 2016;46:139-144.

18. Tamilselvan P, Wang P. Failure diagnosis using deep belief learning based health state classification. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2013;115:124-135.

19. Fakoor R, Ladhak F, Nazi A, Huber M. Using deep learning to enhance cancer diagnosis and classification Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML); 2013 Jun 16-21. Atlanta, GA.

20. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The six Korea National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey 2013-2015 (KNHANES VI) [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention; c2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr

21. Everything About Data Science. Confusion matrix [Internet]. Confusion matrix [Internet]: place unknown: place unknown; c2016. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: http://scaryscientist.blogspot.kr/2016/03/confusion-matrix.html

22. DL4J. Tutorial: deep-belief networks & MNIST [Internet]. place unknown: place unknown: c2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: https://deeplearning4j.org/deepbeliefnetwork.html

23. DL4J. A beginner's tutorial for restricted Boltzmann machines [Internet]. place unknown: place unknown: c2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: https://deeplearning4j.org/restrictedboltzmannmachine

24. History of deep running: site that summarizes the history of deep running [Internet]. place unknown: Jinseob's Home: c2014. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: https://mathemedicine.github.io/deep_learning.html

25. DL4J. Deep learning for Java [Internet]. place unknown: place unknown: c2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: https://deeplearning4j.org

26. Dl4J-examples (Java) [Internet]. place unknown: place unknown: c2017. cited 2017 Oct 1. Available from: https://github.com/deeplearning4j/dl4j-examples

Figure 1
Study design. KNHANES: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, DBN: Deep Belief Network.
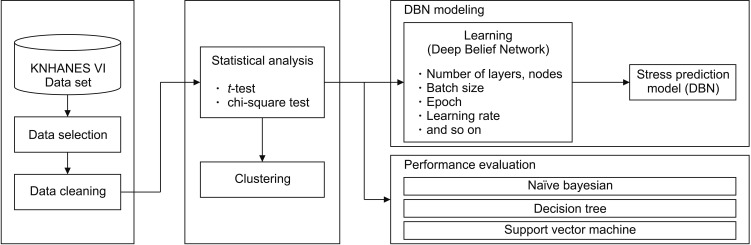
Figure 3
Loss function in terms of profiles: (A) profile 1, (B) profile 2, (C) profile 3, and (D) profile 4.
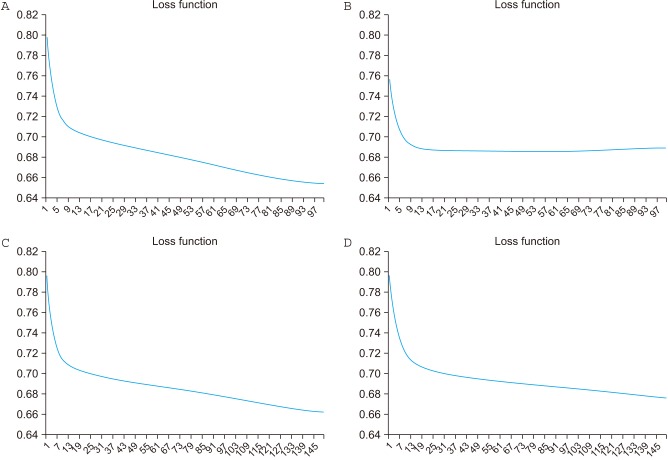
Figure 5
Sensitivity results. NB: naive Bayesian, DT: decision tree, SVM: support vector machine, DBN: Deep Belief Network.
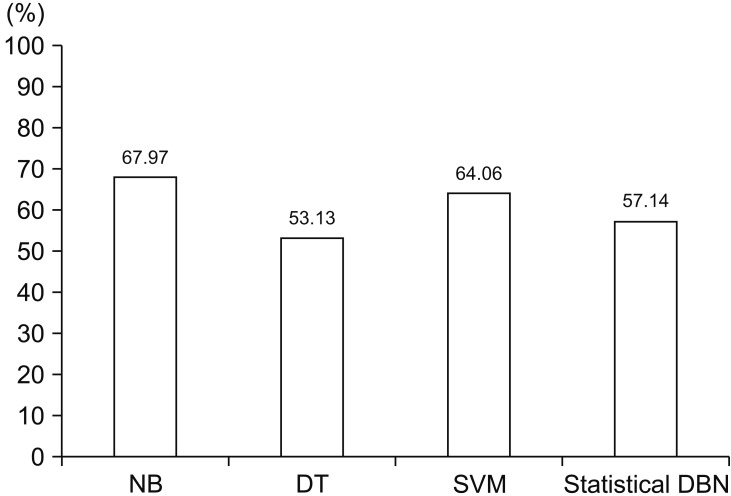
Figure 6
Specificity results. NB: naive Bayesian, DT: decision tree, SVM: support vector machine, DBN: Deep Belief Network.
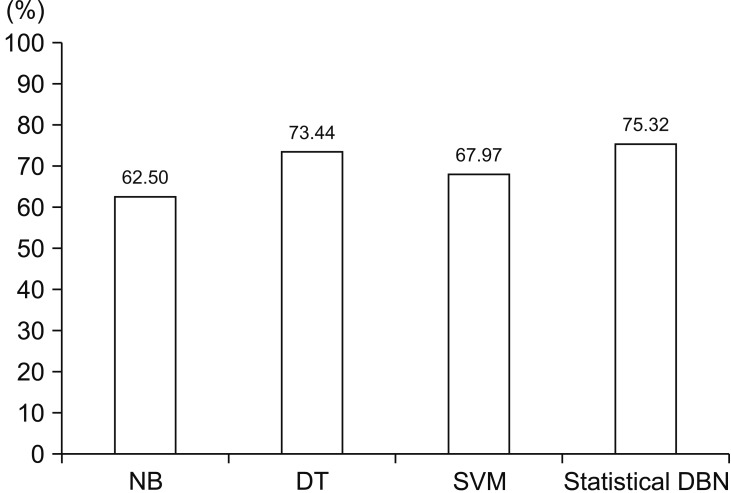
Figure 7
Accuracy results. NB: naive Bayesian, DT: decision tree, SVM: support vector machine, DBN: Deep Belief Network.
-
METRICS

- Related articles in Healthc Inform Res
-
Development of PDA Application Model for Health Promotion Center2009 March;15(1)
Development of a revisit prediction model for the outpatient in a hospital2008 June;14(2)
Development of the Basic DLS Communication Model in Emergency Medical System(EMS)2001 March;7(1)